
Data Analytics & Modelling
Data analytics is the process of gathering data and using it to analyse particular objects in relation to other objects. Often the relationship between two subjects may correlate or disconnect in some circumstances.
Modelling is where data is often analysed. Often visual representations ensure attendees and stakeholders understand the objective view of the data set that is being analysed. The best data analytics is compromised of correct data subjects and expert modelling.
Data & Modelling
Source Data
The very most important part of Data Analytics is the base data. Why, because the base data creates the foundation of accuracy for improvement.
The most important element of the data is the subjects. Usually, data will be collected for the relationship of two or more subject matters (often two).
It is crucial in this stage before collected data, that visually or expressly both data points have a very key influence or effect on one another. The importance of this is that the larger the effect, the larger the reward for resolution.
Data Modelling
Once the data has been collected, it is important to model data correctly.
Often bar and line graphs are an easy tool to show the general population the effect on particular subject matters as this provides a very simplistic visual.
Often more complex scatter plots or choropleth maps are used in more advanced industries and data sets.
The importance of identifying your modelling lies within the test influence that you wish to understand. More complex issues, require more complex data, less complex issues require less complex data.
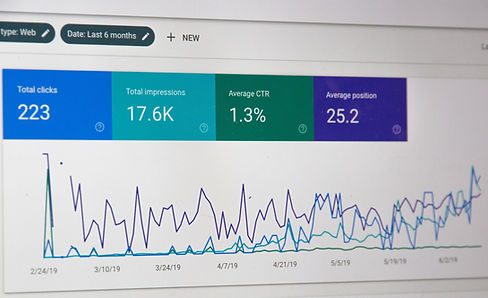

Data Analytics
What Data is Important?
Possibly the most important question when coming to the analytics of data. The importance of having the right data source is written in your net bottom line.
In other words, your base problem solving capability for your product or service must be interrelated heavily to the problem or subject matter that you are trying to solve.
Many companies analyse the wrong subjects, with no real striking improvement variable to the net bottom line.
Analysing Data Correctly
Simply put, as previously discussed, your net bottom line is the baseline of your data.
If your subject is correct, run a few different data sets across the test, and test the results to ensure accuracy in your measurements.
Once this is correctly completed, map out the data and model it in a way which visually enables key stakeholders to understand it.
Next Steps for My Company
Once this is correctly analysed, companies need to the correlate improvement areas.
An improvement area is related to your net bottom line and subject matter. The test variables are the areas that need to be tweaked to ensure a net positive result.